2008 Research
January
The African elephants (Loxodonta africana), Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) and Woolly Mammoths (Mammuthus primigenius) diverged approximately 4-6 million years ago. The exact relationship amongst them has always remained controversial. Morphological studies have suggested a Mammuthus-Elephas clade while several others have supported Loxodonta-Mammuthus clade. Recently, phylogenetic trees based on mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and nuclear DNA sequences of respective elephants, also refuted each other. This has left the phylogenetic relationship between these elephants, unresolved.
The domestic dog is a ubiquitous species having frequent encounters with humans; in the U.S. over 4 million of these result in a dog bite. These injuries might be reduced by improving human-canine communication. Canine responses to alterations of human facial expressions were recorded. The dogs' responses to the presence of a human experimenter were subsequently analyzed against survey data collected by the shelter on the individual animals (time in shelter, age, sex, reason surrendered). Staring at a dog induced more arousal than other human facial expressions (i.e., Averting Eyes, Grinning, or Yawning).
February
A honeybee queen, the only fertile female in a colony, can live up to 47 times as long as her sterile female workers. This contradicts the conventional wisdom of a tradeoff between increased reproduction and improved health and longevity. Whereas most organisms have decreased longevity the more they reproduce, in eusocial insects, especially hymenopterans, this relation is reversed and the individuals that breed more (queens) have longer life-spans than non-reproductives (workers). This discrepancy leads to the question of what might be the physiological mechanism for individuals that reproduce more, outliving by many times individuals that do not reproduce.
The pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN) is a mesopontine nucleus that contains cholinergic neurons and functions as part of the cholinergic arm of the reticular activating system (RAS). It is known to play a critical role in controlling the sleep-wake cycle, locomotor control, and modulation of sensory input. PPN neurons receive somatosensory and auditory input and their output is involved in coordinated flight-or-fight responses. Recent studies show that nicotine reduces the response of a subset of PPN neurons elicited by an unexpected loud sound.
Miniaturization of collagen static tension tissue mold wells can potentially reduce the cost of heart valve tissue culture by lowering reagent usage and cell culture time. Four new well designs with total volumes of 1.34 mL, 0.864 mL, 0.687 mL and 0.202 mL were tested experimentally and statistically compared to the current well design in use, which has a total volume of 2.13 mL. Cardiac aortic valve cells seeded at 1x106 cells/mL and decorin-knocked out fibroblasts seeded at 2x106 cells/mL were used to determine threshold levels in collagen static tension tissue molds where scaffold contraction occurs to a significant and measurable degree without being so forceful that the tissues tear from their anchorage points.
Female mate choice in rodents can be based on genotypic variation among males. Prairie voles (Microtus ochrogaster) exhibit intraspecific variation in the regulatory region of a single gene, avpr1a which encodes the arginine vasopressin 1a receptor (V1aR). Polymorphism in the length of the microsatellite region of the avpr1a gene appears to result in variation in socio-behavioral traits within this species. Males with two long microsatellite alleles have been observed to contribute more time to paternal care and also show a preference toward their partner rather than a strange female relative to males with two short alleles.
Awareness and recollection of surgical events under general anesthesia is an adverse reaction that can lead to psychological disorders including posttraumatic stress disorder. It is estimated that around 0.1% to 0.2% of patients that undergo general anesthesia in the United States are aware of their surroundings and events at some point during their surgery. Awareness under general anesthesia cannot be fully prevented.
March
Eta Carinae is a massive star known for its diverse population of circumstellar ejecta. One specific component of Eta's ejecta with a radial velocity of -513 km/sec has been found to be conducive to the formation of molecules, and CH and OH have most likely been identified there. We first undertook statistical equilibrium modeling with the most recent version of the photoionization code CLOUDY to find the range of physical parameters that would explain the abundances of the observed species in the -513 km/sec component.
Due to the interesting structure, properties and applications of microwires, the electromagnetic properties (DC conductivity, dielectric permittivity and magnetic permeability) of composites with various concentrations of short microwire were investigated for the first time.
Acoustic wave sensors have promising applications in fields such as medicine, law enforcement, and agriculture. In the field of medicine, acoustic wave biosensors can be used to detect the presence of protein markers in patients with certain types of cancer. In developing these devices, resonance frequency tracking is important for testing their functionality. Traditionally, oscillator circuits are used for tracking the resonance frequency of acoustic sensors. However, these oscillator circuits are costly and difficult to adapt to the different frequency ranges of acoustic sensors.
April
This paper analyses the trafficking of children across borders to become prostitutes. This is an important political, economic, and humanitarian issue as large numbers of children in poor countries are lured into the sex trade by unscrupulous traffickers who take advantage of the children's vulnerabilities.
May
Targeted delivery of large therapeutic macromolecules to desired locations inside the brain via systemic delivery is hampered by the function of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), which is formed by tight junctions of the epithelium that lines capillaries in the brain. Recently, direct injection methods such as the so-called Convection-enhanced delivery (CED) are pursued to effectively bypass this vascular barrier and using an infusion catheter whose tip is placed close to the target site. In this technique, a cannula is inserted directly into the area of the brain to be treated, and the therapeutic agent is delivered through the cannula via bulk flow, circumventing the BBB. The efficacy of direct injection methods is assessed by achievable penetration depth and drug distribution volume defined as the region of the brain dosed above a certain therapeutic concentration threshold. In the scope of this paper, the threshold was set at 10% of the inlet drug concentration.
The dynamic interaction between the solid brain, cerebrospinal fluid and blood flow within the cranial vault have previously been described only qualitatively. In this study, computational analysis using the finite element method and physiological parameters was used to describe cerebrospinal fluid-tissue interactions in a quantitative manner. By describing the soft tissue deformations and fluid flow under both normal and pathological conditions, we were able to quantify human intracranial dynamics with the hope of allowing prediction of pathophysiological conditions leading to hydrocephalus or other cerebral disease states.
Urinary tract obstruction is a common clinical problem involving the narrowing of the ureters or urethra. Current diagnostic methods are invasive and costly, and urologists are constantly seeking new, inexpensive, non-invasive measures to diagnose obstruction. The present study investigates diagnostic applications of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to urinary tract obstruction for the first time.
June
Understanding the transport and metabolism of 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine (L-dopa) in the human brain is necessary to better treat people with Parkinson's disease. This disease is caused by an insufficient amount of dopamine (DA) produced in the brain. Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging has been used to study the activity of the dopamine producing enzyme, aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (dopa decarboxylase), in conjunction with a radio labeled analog of L-dopa, 6-[18F]fluoro-L-dopa or F-dopa. In this paper, using reaction coefficients calculated by Gjedde from PET scans, a set of differential equations representing the mass balance of all the reactions and diffusion from L-dopa to dopamine in the blood and brain was created.
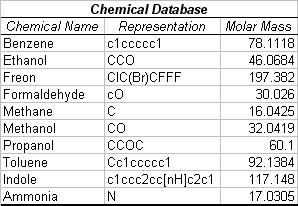
lectronic noses, small electronic instruments with carbon sensing films, provide an artificial version of our olfactory system. In conjunction with pattern recognition techniques, electronic noses can be used to identify odor combinations, perform rudimentary perceptual analysis, and classify unknown odors. Although many different algorithms, from statistical analysis to biologically-inspired neural networks, have been implemented as e-nose pattern recognition techniques, no perfect algorithm has been found. This paper explores the creation and implementation of a novel identification system that uses an outside database to extrapolate the identity of an unknown odor.
Millions of people suffer from various diseases of the central nervous system such as stroke, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and hydrocephalus. To improve the treatment options available, a better understanding of the intracranial dynamics is required. The understanding of intracranial dynamics leads to quantification of fluid flow, cerebrospinal blood pressure, and extension of brain vasculature during the cardiac cycle. One such quantification method, used to simulate the physiological conditions in the brain, is the computer program MATLAB, and one proposed approach is using a "compartmental" model, where arteries, veins, choroids plexus, and other areas and vessels in the brain are lumped as compartments to simulate the intracranial dynamics under normal and hydrocephalic conditions.
July
Although often ignored due to their small size and seeming lack of economic importance, headwater streams have a high ecological importance to watersheds. Although restoration efforts on both streams and rivers have increased in recent years, monitoring on smaller successful and unsuccessful restoration strategies. The purpose of this study is to use macroinvertebrate bioassessment protocols to monitor and gauge the success of a restoration on a flood impaired headwater stream, Smith's Run, within a highly urban watershed.
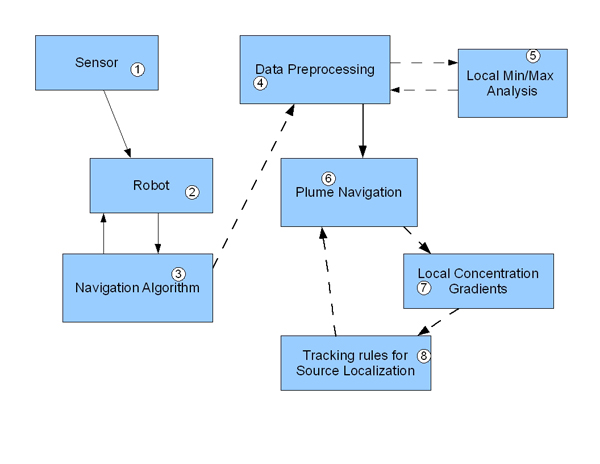
Electronic Olfactory System (EOS) sensor technology is widely used in both research and industry to provide olfactory data for analysis. A variety of physical sensor types exist, each gathering olfactory data in a unique way, and each with individual performance gains and losses. This data has allowed the development of robotic platforms that utilize a variety of algorithms to locate and navigate to the sources of odor plumes in experimental environments. Most of these systems utilize chemotaxis, which allows effective navigation only in ideal, non-turbid environments due to both plume dynamics and limitations in response and recovery times of available artificial olfactory sensors.
August
Oxidative damage of DNA, especially damage induced by singlet oxygen, correlates with a host of disease processes. Due to the link between oxidative DNA damage and disease, a great deal of effort has been put forth to develop methods to detect and quantify DNA damage based on the presence of oxidation-specific biomarkers. Two oxidation products, 8-oxoguanine and 8-oxoadenosine have become important biomarkers of oxidative damage. This study describes a two solution-based methods for monitoring the binding of a fluorescein-labelled avidin to photodamaged lambda phage DNA.
Cocculus cordifolius, a climbing shrub found in tropical Western India, Burma and Ceylon, whose parts are known to be used as traditional herbal medicine to treat various aliments such as cold fevers, seminal weakness and urinary affections, stomach and splenic affections, and chronic gonorrhea. The solvent fractions of the whole plant of C. cordifolius were extracted with hexane, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate and methanol to determine their antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activities.
September
Millions of people suffer from various diseases of the central nervous system such as stroke, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and hydrocephalus. To improve the treatment options available, a better understanding of the intracranial dynamics is required. The understanding of intracranial dynamics leads to quantification of fluid flow, cerebrospinal blood pressure, and extension of brain vasculature during the cardiac cycle.
Electronic noses, small electronic instruments with carbon sensing films, provide an artificial version of our olfactory system. In conjunction with pattern recognition techniques, electronic noses can be used to identify odor combinations, perform rudimentary perceptual analysis, and classify unknown odors. Although many different algorithms, from statistical analysis to biologically-inspired neural networks, have been implemented as e-nose pattern recognition techniques, no perfect algorithm has been found. This paper explores the creation and implementation of a novel identification system that uses an outside database to extrapolate the identity of an unknown odor.
Successful endodontic treatment involves removal of necrotic tissue, bacterial infiltrates, and accumulated procedural debris. However, available irrigants may potentially cause postoperative pain which results in discomfort for the patients. This study aims to evaluate the quality of the current evidences that compared the mildness and antimicrobial activities of the most widely used endodontic irrigants: sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine gluconate. A Timmer analysis is performed in developing a best base series relevant to antibacterial effects of these two root canal irrigants.
October
Using two measures of self-report, we aimed to determine the prevalence of various displays of affection in public places on the campus of the University of the South (Sewanee). A questionnaire was administered to 260 Sewanee students living in dorms on campus and an interview was conducted with a separate, but not necessarily entirely different sample of 140 students. We hypothesized that the college environment of Sewanee would produce a high prevalence of public displays of affection (PDAs) (Afifi and Johnson 1999).
November
Sjogren's syndrome, an autoimmune disease affecting the salivary and lacrimal glands, causes gland degeneration through inflammatory lesions made of lymphocytes. This causes symptoms of dry eyes and mouth. MRL/lpr mice have been used as models of the lymphocytic infiltration characteristic of Sjogren's syndrome, and several immunohistochemical and genetic analyses have been performed on MRL/lpr lacrimal glands.
β-Actin (ACTB) is a ubiquitously expressed cytoskeletal protein. Involved in cell movement and structure, it is usually expressed at constant levels within the cell. We have successfully cloned and sequenced ACTB cDNA from little skate (Leucoraja erinacea) from the 5' untranslated region through the poly-adenylated tail. The deduced protein was 374 amino acids in length, with a 99.7% identity to the human ortholog of ACTB. ACTB is highly conserved among vertebrates and is used as a protein loading control in Western blots and other experiments in which heterogeneous samples are used. In recent years, ACTB has been used as a reference gene in quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) studies where it is used as a control for amplification variations between samples.
December
Many factors affect population dynamics in Daphnia, including the quantity and quality of the algae upon which they feed. A previous study by Urabe and colleagues examined the effects of light and nutrient supply on stoichiometric food quality and showed that, while increased light intensity stimulated increased algae growth, the algae became phosphorus-limited and thus of poor quality due to higher C:P ratios. Furthermore, Urabe's study showed that, under low light, one Daphnia species outcompeted the other, but under high light the two species coexisted.
Microbes and moisture associated with building materials and structures are known to cause health effects. To understand this phenomenon it is important to know how the indoor environment of a moisture damaged building differs from that of a normal and non-damaged building in terms of microbial concentration. In this context, we have selected index and reference buildings based on the criteria like visible mold, smell of mold and moisture damage to compare indoor microbial concentrations of index buildings with that of reference building.