AI’s potential is praised for its capacity to address the scarcity of mental health services and enable more widespread accessibility to healthcare while, in turn, mitigating the risk of burnout among providers. Recent developments have proven AI to be promising in the diagnosis, treatment, and therapy of mental health disorders, with many hailing it as the potential solution to our mental health epidemic. Its potential is so promising that professionals worldwide have already begun implementing it into practice. Nevertheless, there are ethical and societal implications to be considered when we start relying on technology to help us with the one thing it lacks, emotion.
Does Energy From The Air Spell The Future of Sustainability?
We’ve all seen lightning streak through the sky on a stormy night. What we may not know is how that lightning works. In short, the lightning that we see is the product of an electrical charge generated by the water molecules present in the fluffy, white clouds in the sky. What makes it special, though, is that these same water molecules present in humidity are now being explored to harness their conductive capabilities as a potential source of clean energy for the future.
New research suggests potential for repurposing canagliflozin, an anti-diabetic drug, for autoimmune disorders
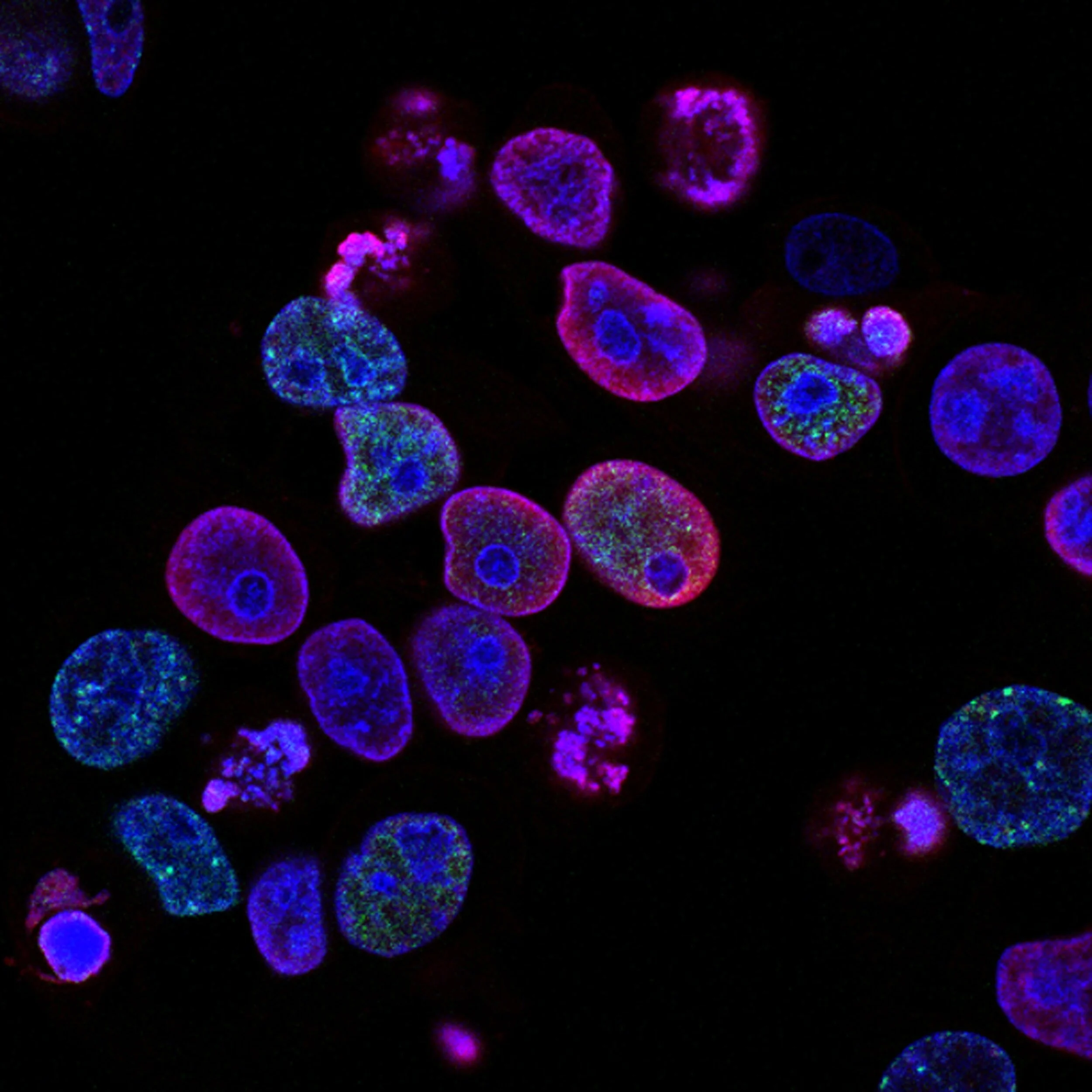
T cells, a component of the adaptive immune system, are involved in autoimmune diseases. Accumulating evidence points to dysregulated T cell metabolism in autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. In the July issue of Cell Metabolism, Jenkins and colleagues investigated the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on T cell function by assessing the levels of inflammatory molecules released, changes in proliferation, gene expression, and metabolism of T cells.