2015 Research
January
February
Author: Charlotte Freeman
Invasive plant species pose a threat to biodiversity worldwide. Ecological disturbances, such as those created by fallen trees, create conditions in which invasive plant species can establish and thrive. This study investigated whether treefall gaps have higher richness of invasive plant species than other areas within forests and potentially serve as a source for the spread of invasive species.
March
Author: Holly D. Thomas
Amputees in underdeveloped areas often do not receive suitable prosthetic devices within the time frame needed for probable success. Typically, prostheses are either not secure or too constrictive of the residual limb. As a result, the constant friction and moisture collection increase the likelihood of skin breakdown. Furthermore, patients living in hot, humid climates are more prone to skin problems due to moisture and lack of proper hygiene. The objective of this project was to create an affordable and modular upper limb prosthetic socket for use by amputees in underdeveloped areas, specifically Brazil.
April
May
June
July
August
Authors: Brittany M. Thornton, Jessie L. Knowlton, Wendy A. Kuntz
Dominance hierarchies have long been observed in nature across many different species. These hierarchies often arise via agonistic behaviors, whereby animals compete for resources while minimizing their physical conflict. Understanding these interactions is important for determining factors that contribute to community structure. We examined interspecific dominance hierarchies of frugivorous neotropical birds at feeding stations baited with bananas in the Wilson Botanical Garden of the Las Cruces Biological Station in Costa Rica.
September
Author: Sajeeda Khan-Woehle
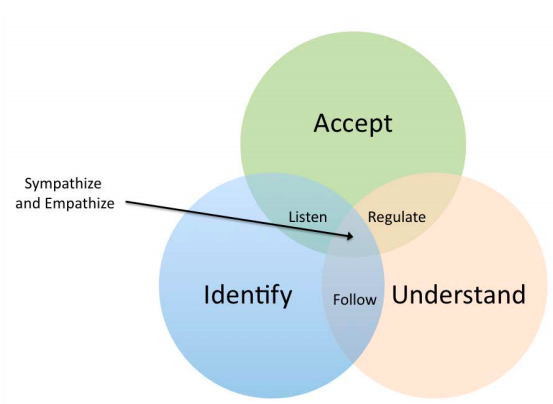
In this exploratory study, a new theoretical model for measuring emotional intelligence, the Emotional Ability Model (EAM), is introduced. The EAM model consists of eight construct areas: identifying, understanding, accepting, following, listening to, and regulating emotions, as well as sympathizing, and empathizing. The EAM model was used to assess emotional intelligence levels of male and female college students at the University of Florida (UF; Gainesville, Florida).
Author: Minna E. Mathiasson
In Africa, stingless bees are greatly understudied organisms that possess incredible ecological and economic potential. Stingless bees are pollinators of tropical plant species and also yield medicinal hive products. Deforestation has caused the preferred habitat of stingless bees to become increasingly rare, forcing populations to relocate. Quality of environment has an immense impact on stingless bee biodiversity and behavior. Therefore it is important to study behavioral changes in different environments. This study aims primarily to explore changes in early colony development of an Afrotropical stingless bee, Hypotrigona sp., when introduced to a new habitat.
Author: Jacob W. Brawer
This study examined the effects of brief exposure to a violent video game on a test of attention and concentration in 12- to 14-year-old males with low-volume video game play histories. We hypothesized that subjects who played 45 minutes of a violent video game would perform significantly worse on a widely-used neuropsychological test when compared to their baseline performance.
October
Authors: Stephen McAuliffe, José Iván Martes Martinez, Laura Warman, and Rebecca Ostertag
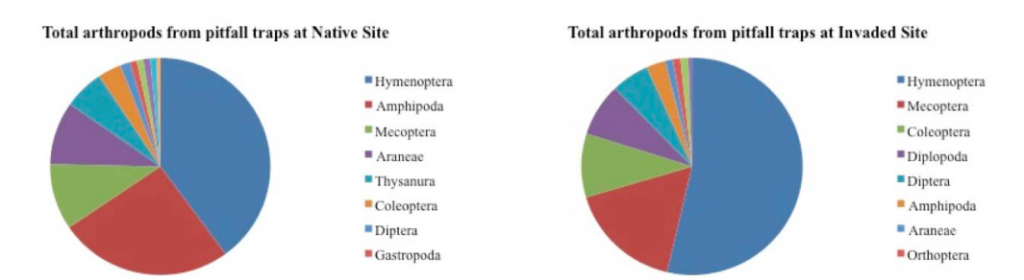
Hawaiian lowland wet forests (HLWF) have been subject to degradation as a result of human activities and the introduction of non-native plant and animal species. Arthropods play crucial roles in forest ecological processes and food web dynamics, and this study aims to compare arthropod diversity and herbivory in HLWF with high or low degrees of invasion. The objective of this study is to test whether invaded HLWF have greater arthropod diversity and therefore higher rates of herbivory than HLWF undisturbed by invasion.
Author: Codey Collins
Prior research has found that progression in and successful completion of drug court programs is linked to mental health factors and various demographics. Little is known, however, about the characteristics and influences of these factors in relation to small rural drug courts, which often consist of a significantly smaller and more homogenous population of participants. This descriptive study examines demographics of a small rural drug court in the southeastern United States.
November
Author: Rachel M. McNeill, William M. DeFoor, Carlos C. Goller, and Laura E. Ott
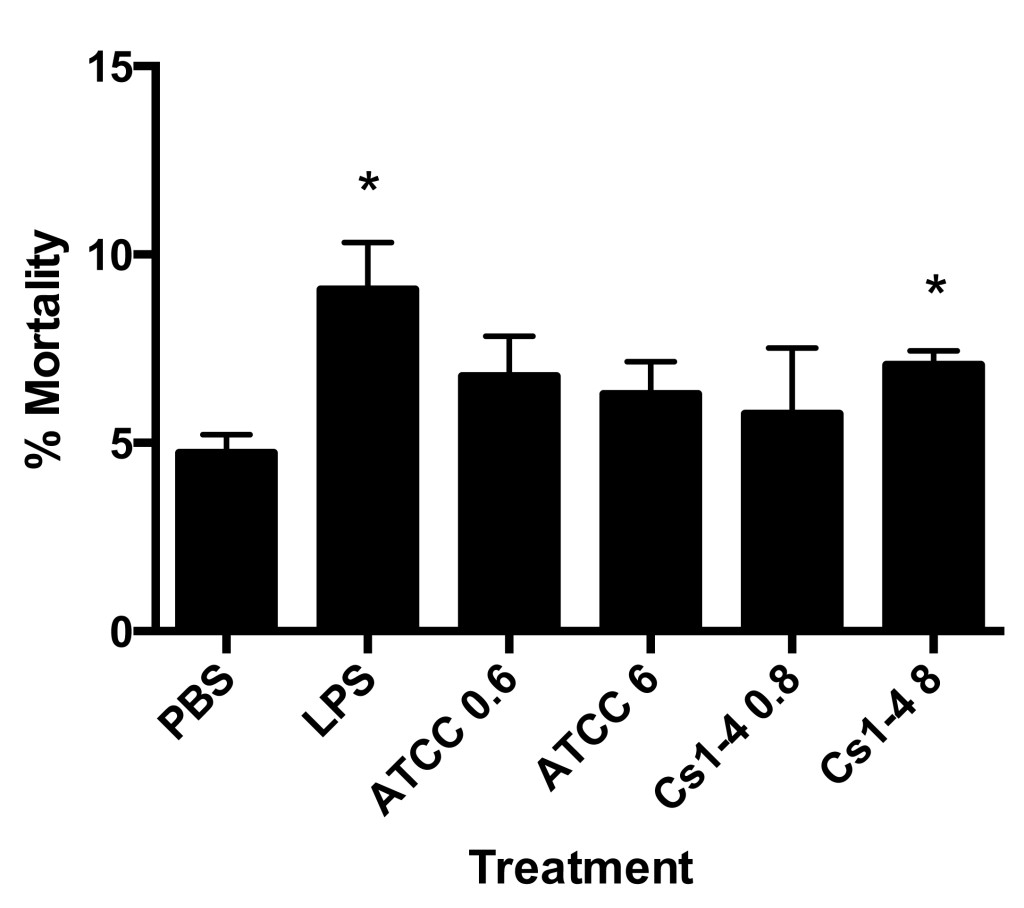
Delftia spp. are rod-shaped, gram-negative water and soil bacteria that are resistant to many commonly used antibiotics. Clinical case reports have described infections of Delftia spp. in patients with intravenous catheters, prompting us to investigate the immune response to Delftia spp. stimulation. We hypothesized that stimulation of THP-1 monocytes with Delftia spp. would elicit a pro-inflammatory response. THP-1 cells were stimulated for 24hr with two strains of heat-killed Delftia spp.: Delftia acidovorans ATCC 13751 at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.6 and 6.0, and Delftia sp. Cs1-4 MOI of 0.8 and 8.0. Purified lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used as the positive control. Stimulation of monocytes with Delftia spp. resulted in increased monocyte mortality.
Authors: Michael O'Brien and Pierre-Richard Cornely
Earthquakes pose a significant threat to human life, especially when they affect major centers of population. However, there is currently no method of predicting seismic activity that gives enough time to prepare for a major catastrophe. This paper presents a method for predicting earthquakes months before an actual seismic event occurs. A major earthquake, which occurred near Haiti’s capitol in early 2010, is investigated using the Detection of Electro-Magnetic Emissions Transmitted from Earthquake Regions (DEMETER) satellite. Electron density in the ionosphere is measured through DEMETER. The electron density measurement is then compared to predictions by the Parameterized Ionospheric Model (PIM), a computer model capable of predicting the electron density at a given point in the atmosphere.