2006 Research
January
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are a suite of 209 possible chlorinated structures, or congeners, having lipophilic properties. They are persistent pollutants that bioaccumulate in the environment and have been suspected to cause a variety of health effects in humans, including cancer. Humans may be exposed to PCBs through consumption of contaminated food items, such as fish, meat and dairy products. Previous studies have shown that fish may contain high PCB levels through exposure to these contaminants in water and ingestion of contaminated prey items. Additional studies suggest that female fish may shunt PCBs from their body via roe production. The objective of this study was to quantify the presence and levels of 110 PCB congeners in six roe samples commonly sold as caviar.
February
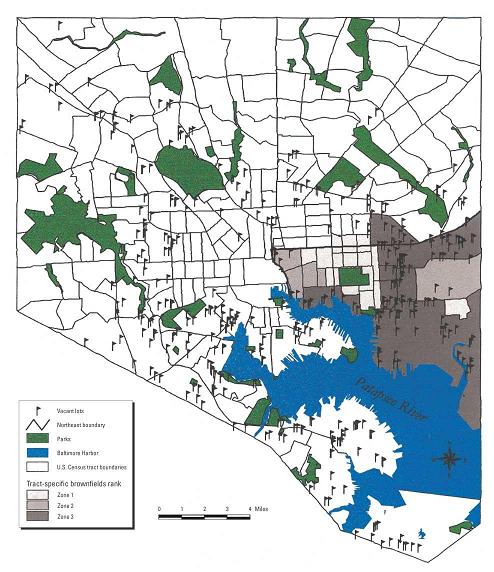
Many American cities, such as Baltimore, are facing modern dilemmas while transitioning from industrial to service-based economies. However, the decline of industry has left many cities with acres of abandoned and potentially contaminated tracts of land, called brownfields, which may pose hazards to human health. Thus, to explore potential hazards, urban economic impact, and strategies for revitalization- we conduct an in-depth case review of the brownfield situation in Baltimore, Maryland. We conducted a systematic review of MEDLINE from 1965 to 2003 to identify all relevant publications.
March
The amino acid sequence of the enzyme coproporphyrinogen oxidase (copro'gen oxidase) in the heme biosynthetic pathway is known but its catalytic mechanism has yet to be determined. As a result, it is essential to carry out site-directed mutagenesis on highly conserved amino acids to help determine which amino acids are essential for catalysis. Often, a large number of mutants are created in this fashion, so it is in the researcher's best interest to have a technique to evaluate such mutants efficiently, quickly, and cheaply.
April
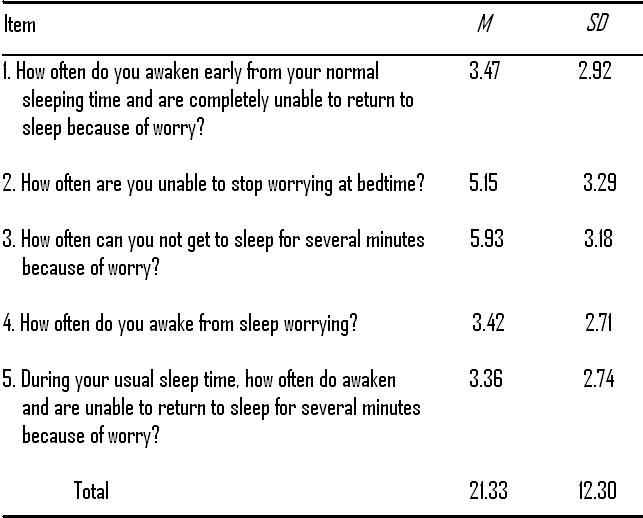
Psychologists have devoted little attention to contemplating the effect of worry on the sleep patterns of college students. The purpose of this study is to address this gap by focusing on academic worries and its effect on length of sleep. It was proposed that students who have more academic worries would report less sleep than those who have less academic worries. It was also proposed that an increase in sleep disturbances attributed to worry would predict less sleep.
May
Early Childhood Caries (ECC) is a chronic and infectious oral disease of young children, most commonly seen in poor and minority populations. Factors such as improper feeding practices, familial socioeconomic background, lack of parental education and dental knowledge, and lack of access to dental care can contribute to and explain why the prevalence of ECC is so great in these select populations. Current research has shown that parents and caretakers have a huge impact on the success of preventative methods and the prevention of ECC altogether. Preventative methods include restorative dental care that focuses on the disease component of ECC, and behavioral and educational programs that advocate individualistic changes so that parents and caretakers can detect and avoid the reoccurrence of caries in their children.
June
July
August
In this paper, we modeled the progressive loss of declarative memory in Alzheimer's disease (AD) using an artificial neural network (ANN) framework. Declarative memory is associated with tasks involving recognition. Furthermore, we modeled the declarative memory in a healthy individual as a fully connected Hopfield neural network. Memory loss in the healthy memory models was implemented by resetting randomly selected synaptic weights to 0'. Unhealthy memory models were created by damaging the healthy Hopfield memory models by a percentage of the weights. Recognition of the memory models was evaluated using recall/response rates. In the neural model, the detection of optimal network architectures was crucial. The paradigm that we have identified has three critical phases. The detection of neural synaptic promoters in the neural network was extremely imperative in the first phase of the investigation. In order to determine this, the network was trained on datasets and corresponding recall/response rates were observed. The second facet of the experiment involved the evaluation of different ANN's by which the optimal network architecture could be identified. And finally, the third facet, involved the detection of areas where synaptic connectivity was affected and where it could be improved.
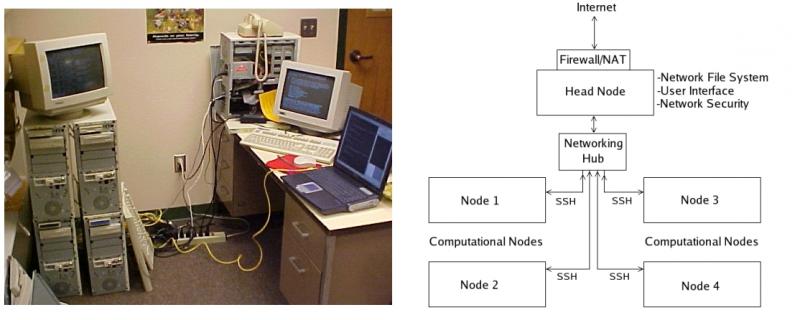
This experiment examined the overall times required to make messaging calls in parallel programs within a distributed computing environment. These messaging calls are defined in the Message Passing Interface (MPI) standards, which is a set of recommendations for designing communication calls for parallel programs. Different libraries based on the MPI standards exist, and this project focused on two commonly used implementations: MPICH and LAM-MPI. Both provide the same essential methods and functions, but their package and algorithm structures differ enough so that the administrative, processing, and messaging times of a program may be improved by selecting one package over the other. With adequate foreknowledge of the strengths and weaknesses of the MPI packages, programmers and administrators can better select a package based on their needs.
Fat has been termed the "new tobacco" by the Canadian Heart and Stroke Foundation, because of the high general risk of an individual eventually becoming obese. This review will discuss the cause and effect of childhood obesity as well as compile recommendations and initiatives currently in place to decrease childhood and adult obesity. For children of the 21st century, obesity is one of the most common metabolic and nutritional diseases. Healthcare professionals can measure the percent of body fat in children by using Body Mass Index (BMI). Specifically, for children and BMI that is age and gender specific can be used to take measurements of the percent of body fat. Researchers have identified three main causes of obesity and they include genetics, overeating and lack of exercise. The effects of obesity on children have a huge impact and can range from low self-esteem to increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. The most effective cure for childhood obesity is prevention. Parents and healthcare professionals can work together to make prevention more effective and one day perhaps abolishing this epidemic.
September
Larvae of Chaoborus species are voracious predators of zooplankton in aquatic ecosystems, capable of altering the species composition and size structure. To estimate the impact of Chaoborus larvae on zooplankton in Campus Lake, Jackson Co. IL, a 24-hour field survey and a controlled predation experiment in the laboratory were conducted. Specifically, the hypothesis tested was that Chaoborus larvae select Daphnia over copepods, two zooplankton taxa on which the larvae are known to feed and which occur in Campus Lake.
The tropical forest canopy is a unique ecosystem with complex environmental interactions, which allows for a high level specialization of insects. The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether in creased species specialization has created species variation between nocturnal and diurnal canopy insects. Insects were collected from six trees using suspended traps containing three types of bait (carrion, rotten fruit, and scents).
October
De novo designed peptide nanoparticles can have the size of a virus and carry antigenic information on their surface. Through genetic engineering, it is possible to mount almost any peptide-based epitope on the surface of the nanoparticles. In theory, the nanoparticles can elicit an immune response when used as a vaccine. Burkhard et. al. have designed such a peptide nanoparticle that consists of 60 peptide monomers and which has a diameter of about 20 nm. Our goal was to develop a novel Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) vaccine by mounting HIV epitopes on the surface of the nanoparticles. In this project, the forward and reverse strands of DNA oligomers that coded for a highly conserved portion of the HIV protein gp41 were annealed. The annealed oligomers were successfully ligated into the expression vector pP_3a that coded for the peptide monomer of the core particle. The recombinant DNA was transformed into the Escherichia coli strain BL21(DE3)pLysS and the bacteria were cloned.
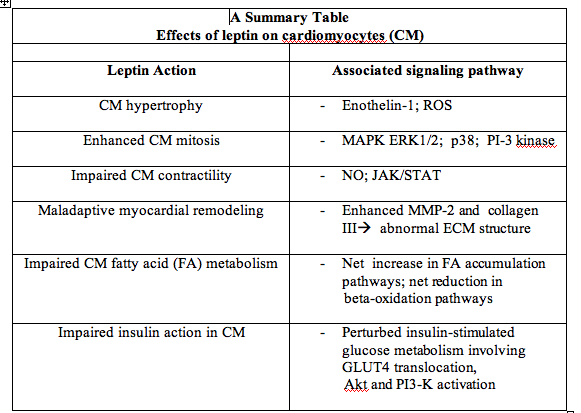
Obesity has been linked to the pathogenesis of heart failure. Leptin, a 16-kD peptide hormone synthesized mainly by the adipocytes reduces food consumption and enhances energy expenditure. Leptin receptors (Ob-R) consist of six isoforms (ObRa-ObRf) and are present mainly in the hypothalamus as well as other tissues. Leptin deficiency and resistance have been implicated in the development of left ventricular hypertrophy and myocardial infarction. Impaired leptin action can also affect insulin sensitivity in cardiomyocytes leading to development of heart failure. The effects of leptin on cardiomyocytes have not been analysed in a comprehensive manner. This review explores how leptin-induced signaling pathways and leptin deficiency or resistance can promote heart failure by promoting cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, maladaptive vascularremodeling, impairing cardiac contractility, and perturbing fatty acid metabolism in cardiac myocytes.
Polylactide can be processed into fibers and films for various biomedical applications, including sutures, dialysis media, and drug delivery devices. In this work, well-defined biodegradable polylactide (PLA) containing block copolymers, poly(ethylene-co-1,2-butylene)-b-poly(D-lactide) (PEB-b-PDLA) and poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(L-lactide) (PEO-b-PLLA), were synthesized via ring-opening polymerization of D- and L-lactides initiated from PEB-OH and PEO-OH macroinitiators, respectively. The goal of this research was to obtain stereocomplexes from PLA block copolymers containing highly immiscible blocks such as hydrophilic PEO and hydrophobic PEB.
We have recently defined a concise, three-step synthesis to carbohydrate-based oxepines from pyranose lactols, where the key step involved a Schrock catalyst mediated ring closing metathesis (RCM) reaction. A sub-family of diene substrates could be cyclized using the Grubbs second-generation catalyst, although the yields were low (25-30%) and a side product, tri-O-benzyl glucal was observed (~10%). The present study was undertaken to find a cleaner and more efficient route of synthesizing oxepines.
The study of fatigue is of major engineering importance because cracks occur more frequently than expected. The goal of this research is to be able to better predict fatigue crack growth (FCG) in 2324 Aluminum Alloy. Being able to accurately determine FCG will help prevent disastrous failure of engineering structures. Through the experimentation of a varying stress intensity factor with a constant stress ratio and constant amplitude loading, a better understanding of FCG is anticipated. Due to time constraints, only the stress ratio of 0.1 was tested for this paper. However, the resulting data from the test was compared with previous data obtained from the exact same test setup, and it was found to be comparable.
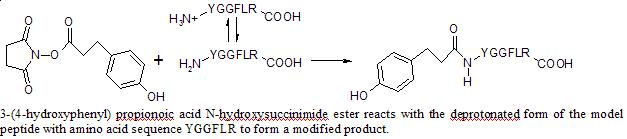
The bioconjugation of a protein with an N-hydroxysuccinimide ester is a protein modification technique used to create biomedical and biotechnological products. Some of the difficulties in this type of protein modification reaction are that proteins have many amines which react with N-hydroxysuccinimide esters, and the reaction solutions are difficult to analyze due to the complexity of the components. This study tests on a small scale whether controlling the pH could potentially be used to improve the site specificity of a protein modification reaction.
November
In 1972, Carijoa riisei, a shallow-water azooxanthellate octocoral, was discovered invading the fouling community in Pearl Harbor. Invasive populations of C. riisei are now so dominant that they are considered a grave threat to Hawaii's native reef ecosystems and economy. C. riisei's juvenile and reproductive biology is not very well understood because of the difficulty of field observations at the depth that C. riisei inhabits. A laboratory based culture technique would represent a significant advancement in our ability to investigate questions involving the spread and control of C. riisei. Flow-through aquariums were set-up to house captive C. riiseicolonies over a period of seven weeks. C. riisei colonies were successfully grown on freeze-dried copepods and exhibited release of gametes. The success of this culturing method bodes well for long-term maintenance of C. riisei and further experiments with C. riiseibiology.
Staphylococcus aureus is an opportunistic human pathogen that is found in a large percentage of the population and passively colonizes primarily in the skin or in the nares. It is also occasionally found in high abundance in coastal recreational waters due to shedding from swimmers and other beachgoers. As a result, coastal swimming areas are a potential source of community-acquired S. aureus infections. The capacity of a given S. aureus strain to cause infection varies among strains and is determined by the presence or absence of a large number of virulence-associated genes, some of which are encoded by prophages. In order to determine the abundance and characterize the diversity of S. aureus strains to which swimmers in coastal waters of Oahu may be exposed, 30 isolates were collected from seawater at Kuhio Beach in Waikiki, HI and screened for the presence or absence of phage-type specific DNA segments using polymerase chain reaction. One to five prophage segments were detected per isolate with no prophage-free strain found. Prophage segments from ø3A-like and ø77-like phages were most common, showing up in nearly all isolates collected. Data from this study suggests that prophage content in S. aureusisolates varies widely among strains and the diversity at Kuhio Beach is relatively high.
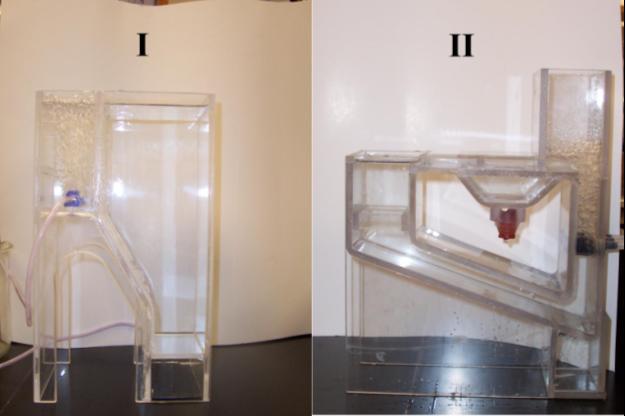
Studies have shown that the use of copepod nauplii as a first feed will increase the survival rate of larvae of several ornamental finfish species, and it is widely agreed that the use of copepod nauplii as a first feed will increase the number of ornamental species which can be successfully cultivated. Many bioreactors have focused on producing live nauplii, but problems arise because the nauplii grow too quickly. To circumvent this problem, we propose a novel airlift bioreactor design to support the collection and preservation of copepod eggs. In most cases, airlift columns are used in bioremediation to suspend pellets for the growth of biofilm. In this case, airlift columns are used to both aerate and to separate copepod eggs from adults into a collection chamber.
Mycoplasma arthritidis-derived Mitogen (MAM) is a superantigen that can dimerize major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigen, HLA-DR1 molecule. MAM is known to induce chronic arthritis in rodents which bear a resemblance to human rheumatoid arthritis. MAM stimulates T-cell activation by interacting with class II MHC including HLA-DR1, which is one of the important disease risk genes in rheumatoid arthritis. It has been suspected that MAM a plays role in human rheumatoid arthritis. The high affinity of MAM to the peptide/MHC complex is due to interaction between the N-terminal domain of MAM and the antigen-presenting domain of MHC. In this study, we created mutants at the N-terminal domain of MAM to investigate the MAM residues responsible for this interaction. We mutated four amino acids: threonine, arginine, lysine and glutamine at positions 89, 91, 92, and 99, respectively. The four residues, which are at the MAM-MHC interface, were individually converted to alanine. Sedimentation velocity of analytical ultracentrifuge was used to identify the heterogeneous interaction between the mutant and the MHC molecule. The dissociation constants (KD) of the mutant MAM-MHC complexes were measured using sedimentation equilibrium. Of the four mutants, R91A binds to HLA DR1 with the lowest affinity, which is about twenty times lower than that of the wild-type. Other mutants reduce the binding affinity of MAM to HLA DR1 by 7-10 folds. These data provide evidence that substitution of any of these four residues will cause the affinity of MAM to the peptide/HLA-DR1 complex to decrease.
December
Invasive Asian earthworms (Amynthas hilgendorfi and A. agrestis) have transformed forest ecosystems along the eastern seaboard of the United States by decimating the forest leaf litter layer, shifting nutrient cycles, and altering belowground fine root distributions and microbial dynamics. Natural resource managers are looking for management methods that both control invasive earthworm populations and ameliorate their damaging effects on the forest ecosystem. Healthy fungal populations in forest soils are particularly important for the successful establishment and growth of plants and tree seedlings in reforestation efforts. The purpose of this study is to examine the impact on soil microflora of earthworm control treatments in an urban forest restoration project.
The coastal area of Hilo, Hawaii are dotted with estuarine ponds with varying degrees of influence by input of terrigenous water by run-off and ground water. These estuarine ponds are popular for recreational uses such as swimming and collection of benthic diatom, Melosira sp. as fishing bait. The purpose of our study is to determine if the ponds act as a buffer zone for the adjacent coral formations and to generate a baseline data set of the water quality of these ponds and compare the bacterial concentrations to the Hawaii Department of Health (HDOH) and national Environmental Protection Agency standards. Nutrient levels, Clostridium perfringens and Enterococcus faecalis concentrations within the ponds were monitored and surveys of benthic macroalgae and invertebrates were conducted monthly from September 2005 to March 2006. Nutrient concentrations varied spatially and temporally. Benthic flora and fauna cover and assemblage varied temporarily within ponds and spatially between ponds. The microbe levels also showed high frequency and range of concentrations. The concentrations of C. perfringens and E. faecalis were consistently higher than the state standards some as much as eight times as high.
Sponges are a prolific source of biological compounds with diverse bioactivities. However, structural similarities between the metabolites of the sponge and its associated bacteria, those found within its tissue, indicate that these compounds are of bacterial origin. 16S rRNA gene sequence analyses have been widely used to identify and characterize both culturable and unculturable populations of marine bacteria. The purpose of this research was to isolate sponge-associated bacteria and screen them for antibacterial activity. In this study, a total of 178 potentially different bacteria were isolated from the Hawaiian sponge Suberites zeteki. Due to time restrictions, only the first forty of the bacterial isolates were subjected to further analyses. 16S rRNA gene analyses identified many isolates with a diversity of bacterial groups, including the genus Bacillus and Vibrio. Three of the seven representative bacterial isolates tested inhibited the growth of Bacillus subtilis, a microbe commonly used in bioactivity screening.
The emergence of antibodies as immunotherapeutic agents has offered a tremendous new potential for the treatment of a multitude of human illnesses and diseases. The use of antibodies offers target specificity unparalleled in conventional treatments and therapies. Generation of monoclonal antibodies was made possible by the development of hybridoma technology. Subsequent advances in the development of phage and transgenic mouse technologies have allowed the generation of fully humanized antibodies. Antibody based therapies have used naked antibodies as therapeutic agents or conjugated them with other therapeutic agents such as toxins, radionuclides, and enzymes.